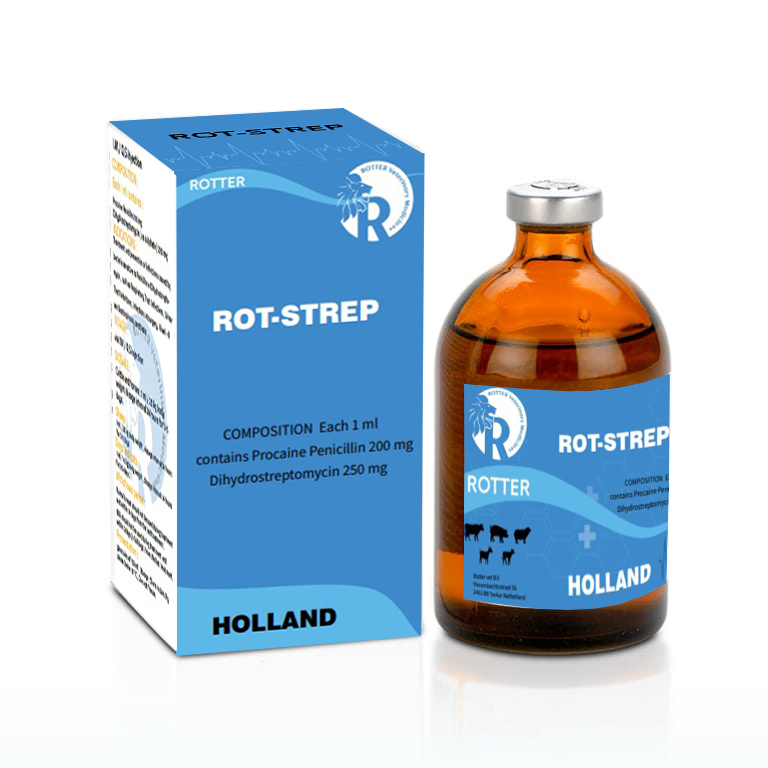
ROT – STREP
Contains per ml:
Procaine penicillin G ………………………………………… 200 000 IU.
Dihydrostreptomycin sulphate ………………………….. 200 mg.
Solvents ad …………………………………………………….. 1 ml.
Procaine penicillin G ………………………………………… 200 000 IU.
Dihydrostreptomycin sulphate ………………………….. 200 mg.
Solvents ad …………………………………………………….. 1 ml.
Arthritis, mastitis and gastrointestinal, respiratory and urinary tract infections caused by
penicillin and dihydrostreptomycin sensitive micro-organisms, like Campylobacter, Clostridium,
Corynebacterium, E. coli, Erysipelothrix, Haemophilus, Klebsiella, Listeria, Pasteurella,
Salmonella, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp. in calves, cattle, goats, sheep and swine.
penicillin and dihydrostreptomycin sensitive micro-organisms, like Campylobacter, Clostridium,
Corynebacterium, E. coli, Erysipelothrix, Haemophilus, Klebsiella, Listeria, Pasteurella,
Salmonella, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp. in calves, cattle, goats, sheep and swine.
The combination of procaine penicillin G and dihydrostreptomycin acts additive and in some
cases synergistic. Procaine penicillin G is a small-spectrum penicillin with a bactericidal action
against mainly Gram-positive bacteria like Clostridium, Corynebacterium, Erysipelothrix, Listeria,
penicillinase-negative Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp. Dihydrostreptomycin is an
aminoglycoside with a bactericidal action against mainly Gram-negative bacteria like E. coli,
Campylobacter, Klebsiella, Haemophilus, Pasteurella and Salmonella spp.
Hypersensitivity to penicillins, procaine and/or aminoglycosides.
Administration to animals with a seriously impaired renal function.
Concurrent administration of tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, macrolides and lincosamides.
Administration to animals with a seriously impaired renal function.
Concurrent administration of tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, macrolides and lincosamides.
For intramuscular administration:
Cattle: 1 ml per 20 kg body weight for 3 days.
Calves, goats, sheep and swine: 1 ml per 10 kg body weight for 3 days.
Shake well before use and do not administer more than 20 ml in cattle, more than 10 ml in swine
and more than 5 ml in calves, sheep and goats per injection sit e.
Cattle: 1 ml per 20 kg body weight for 3 days.
Calves, goats, sheep and swine: 1 ml per 10 kg body weight for 3 days.
Shake well before use and do not administer more than 20 ml in cattle, more than 10 ml in swine
and more than 5 ml in calves, sheep and goats per injection sit e.
– For kidney: 45 days.
– For meat: 21 days.
– For milk: 3 days.
– For meat: 21 days.
– For milk: 3 days.
Administration of therapeutic dosages of procaine penicillin G can result in abortion in sows.
Ototoxity, neurotoxicity or nephrotoxicity.
Hypersensitivity reactions.
Ototoxity, neurotoxicity or nephrotoxicity.
Hypersensitivity reactions.
Vial of 50 and 100 ml.